[ad_1]
The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) represents a significant leap forward in AI capabilities. These models have advanced to a point where they can generate text, interpret images, and even understand complex multimodal inputs with sophistication that closely mimics human intelligence. However, as the capabilities of these models have expanded, so too have the concerns regarding their potential misuse. A particular concern is their vulnerability to jailbreak attacks, where malicious inputs can trick the models into generating harmful or objectionable content, undermining the safety measures to prevent such outcomes.
Addressing the challenge of securing AI models against these threats involves identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit. The task is daunting; it requires a nuanced understanding of how AI models can be manipulated. Researchers have developed various testing and evaluation methods to probe the defenses of LLMs and MLLMs. These methods range from altering textual inputs to introducing visual perturbations designed to test the models’ adherence to safety protocols under various attack scenarios.
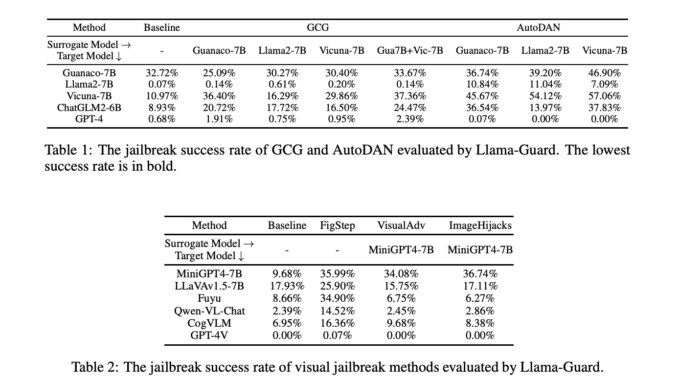
Researchers from LMU Munich, University of Oxford, Siemens AG, Munich Center for Machine Learning (MCML), and Wuhan University proposed a comprehensive framework for evaluating the robustness of AI models. This framework involves the creation of a dataset containing 1,445 harmful questions spanning 11 distinct safety policies. The study employed an extensive red-teaming approach, testing the resilience of 11 different LLMs and MLLMs, including proprietary models like GPT-4 and GPT-4V, as well as open-source models. Through this rigorous evaluation, researchers aim to uncover weaknesses in the models’ defenses, providing insights that can be used to fortify them against potential attacks.
The study’s methodology is noteworthy for its dual focus on hand-crafted and automatic jailbreak methods. These methods simulate a range of attack vectors, from inserting harmful questions into templates to optimizing strings as part of the jailbreak input. The objective is to assess how well the models maintain safety protocols despite sophisticated manipulation tactics.
The study’s findings offer insights into the current state of AI model security. GPT-4 and GPT-4V exhibited superior robustness to their open-source counterparts, resisting textual and visual jailbreak attempts more effectively. This discrepancy highlights the varying levels of security across different models and underscores the importance of ongoing efforts to enhance model safety. Among the open-source models, Llama2 and Qwen-VL-Chat stood out for their robustness, with Llama2 even surpassing GPT-4 in certain scenarios.
The research contributes significantly to the ongoing discourse on AI safety, presenting a nuanced analysis of the vulnerability of LLMs and MLLMs to jailbreak attacks. By systematically evaluating the performance of various models against a wide range of attack methods, the study identifies current weaknesses and provides a benchmark for future improvements. The data-driven approach, incorporating a diverse set of harmful questions and employing comprehensive red-teaming techniques, sets a new standard for assessing AI model security.
Research Snapshot

In conclusion, the study conclusively highlights the vulnerability of LLMs and MLLMs to jailbreak attacks, posing significant security risks. Establishing a robust evaluation framework, incorporating a dataset of 1,445 harmful queries under 11 safety policies, and applying extensive red-teaming techniques across a spectrum of 11 different models provides a comprehensive assessment of AI model security. Proprietary models like GPT-4 and GPT-4V demonstrated remarkable resilience against these attacks, outperforming their open-source counterparts.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter. Join our Telegram Channel, Discord Channel, and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 39k+ ML SubReddit
![]()
Hello, My name is Adnan Hassan. I am a consulting intern at Marktechpost and soon to be a management trainee at American Express. I am currently pursuing a dual degree at the Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. I am passionate about technology and want to create new products that make a difference.
[ad_2]
Source link

Be the first to comment